18 YEARS EXPERIENCE
We are a professional supplier of a variety of gas chemical products to meet your various needs.
Products Description
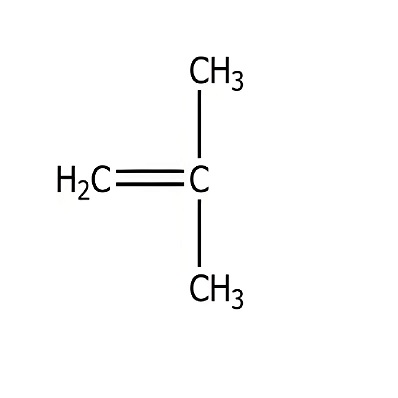
Product Name:Isobutylene
CAS:115-11-7
Molecular formula:C4H8
Molecular weight:56.11
EINECS:204-066-3
Introduction
Isobutylene is also known as 2-methylpropylene. In industry, isobutylene is almost always obtained from refinery gas and cracking C4 fraction. The isobutylene content in refinery gas is generally 5% to 12%, and in cracking C4 fraction it is generally 20% to 30%.
Isobutylene Chemical Properties
| Melting point | −140 °C |
| Boiling Point | −6.9 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.5879 |
| Vapor density | 2 (vs air) |
| Vapor Pressure | 3278 mm Hg ( 37.7 °C) |
| Refractive Index | 1.3811 |
| Flash point | -80 °C |
| Form | Transparent liquid |
| Color | Colorless to almost colorless |
| Odor Threshold | 10ppm |
| Water solubility | 263mg/L(25 ºC) |
| Freezing point | -140.34℃ |
| Merck | 14,5141 |
| BRN | 773645 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 0.20, 0.26, 0.33, and 0.41 at 30, 40, 50, and 60 °C, respectively (Leung et al., 1987:Zhang et al., 2002) |
| Stability | Stable. Highly flammable. Can easily form explosive mixtures with air. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
Chemical properties
Isobutylene is a colorless gas, m.p.-140.35℃, b.p.-6.8℃, n25D1.381, relative density 0.673 (-49℃), 1.998 in gaseous state, can form explosive mixture with air, explosion limit 1.7%~9.0% (volume fraction), soluble in organic solvents, easy to polymerize.
Applications
The chemical utilization of isobutylene can be divided into two categories: one is the direct utilization of mixed C (extracted butadiene) fractions and the processing utilization of high-purity isobutylene.
Uses
1. Isobutylene, also known as 2-methylpropene, is an important petrochemical raw material. In the pesticide industry, it is mainly used to prepare organophosphorus insecticide terbuthion, pyrethroid insecticide permethrin and acaricide pyridaben. At the same time, isobutylene is also widely used in light industry, oil refining, medicine, spices, building materials and other fine chemical sectors.
2. In industry, high-concentration isobutylene is mainly used to produce polyisobutylene and copolymerize with isoprene to produce butyl rubber. Isobutylene and isobutane can be alkylated to produce high-octane alkylated gasoline, and methyl tert-butyl ether obtained by reaction with methanol is an excellent gasoline additive. It is also suitable as an alkylation raw material for aromatics, or fine chemicals produced by oxidation, amination and other operations. The derivative of isobutylene, 2-tert-butyl-p-cresol, is coupled with 2-nitro-5-chloroaniline diazotide and then reduced to obtain 2,3'-tert-butyl-2'hydroxy-5'-methylphenyl-5-chlorobenzotriazole, which is a good ultraviolet absorber. In addition, o-tert-butylphenol can be nitrated to obtain 2-tert-butyl-4,6-dinitrophenol, which is an agricultural herbicide.
3. Adding water can produce tert-butyl alcohol, oxidizing to produce methacrolein and methacrylic acid, and ammoxidizing to produce methacrylonitrile, etc.
Production method
1. Isobutylene is almost always obtained from refinery gas and cracking C4 fractions in industry. The isobutylene content in refinery gas is generally 5%-12%, and in cracking C4 fractions it is generally 20%-30%. In a few cases, it is obtained by catalytic hydrogenation of isobutane using chromium oxide-alumina catalyst. When propylene and isobutane are used as raw materials to produce propylene oxide by co-oxidation, isobutylene is a co-product.
2. There are many methods for preparing isobutylene. At present, the main method used in production is the methyl tert-butyl ether etherification method, that is, isobutylene is obtained by catalytic etherification of methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE). (CH3)3COCH3[catalyst]→(CH3)2C=CH2+CH3OH The catalysts used in the catalytic etherification reaction include Al2O3, sulfate, phosphate, uranium oxide and hydroxide, and activated carbon. The reaction temperature is 150-300°C, the reaction pressure is 0.3-0.6MPa, and the liquid volume space velocity is 1-5h-1. When modified Al2O3 is selected as the catalyst and the temperature is 180°C, the isobutylene recovery rate reaches 100%. In addition, there are also sulfuric acid absorption or hydrochloric acid absorption separation from the C4 fraction, isobutane dehydrogenation, tert-butyl alcohol dehydration, ion exchange, adsorption, selective polymerization separation, etc.
OUR ADVANTAGE
 18 YEARS EXPORT
18 YEARS EXPORT QUALITY CERTIFICATES
QUALITY CERTIFICATES OEM/ODM SUPPORT
OEM/ODM SUPPORT QUALITY CERTIFICATES
QUALITY CERTIFICATES OEM/ODM SUPPORT
OEM/ODM SUPPORT QUALITY CERTIFICATES
QUALITY CERTIFICATES