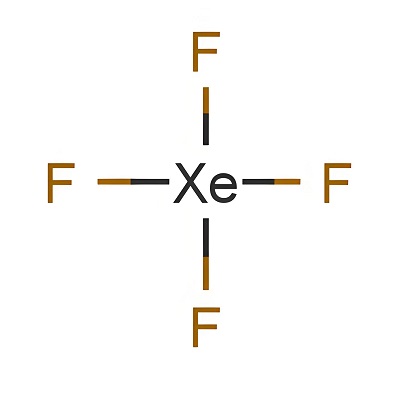About Us
Shandong Deshang Chemical Co., Ltd. is a new chemical enterprise specializing in the supply of gas chemicals. We specialize in the supply of various gas chemical products, ethyl chloride, xenon, sulfur dioxide, ethylene and other products with sufficient inventory. Our cooperative customers are all over the world, such as Europe, Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Africa, the United States, Australia and other countries and regions.Our company currently has more than 200 employees, with an office,...
read more Why choose us
The chemical raw materials we provide are strictly tested according to international standards to ensure high quality and stability.
Product quality assurance
The chemical raw materials we provide are strictly tested according to international standards to ensure high quality and stability.
Rich product lines
Covering multiple chemical fields, meeting the one-stop procurement needs of customers in different industries.
Competitive prices
hrough large-scale procurement and cost control, we provide market-competitive prices.
Flexible supply chain management
Quickly respond to market demand, ensure timely delivery, and reduce customer inventory pressure.
Excellent Technology
Always adhere to adopting our own proprietary technology in core technology.
Professional technical support
An experienced team provides technical consultation and after-sales service.
The perfect combination of quality and service to help you succeed
News